What is an acceptable or good profit margin in one industry may be terrible or ridiculously high in another one. There are other key profitability ratios that analysts and investors often use to determine the financial health of a company. During the month of January, your total revenue was $50,000, and your cost of goods sold was $15,000. Because companies express net profit margin as a percentage rather than a dollar amount, it is possible to compare the profitability of two or more businesses regardless of size. Best practices when using the Percentage of Net Sales Method include regularly monitoring sales figures and inventory levels to ensure accurate reporting and compliance with tax regulations.
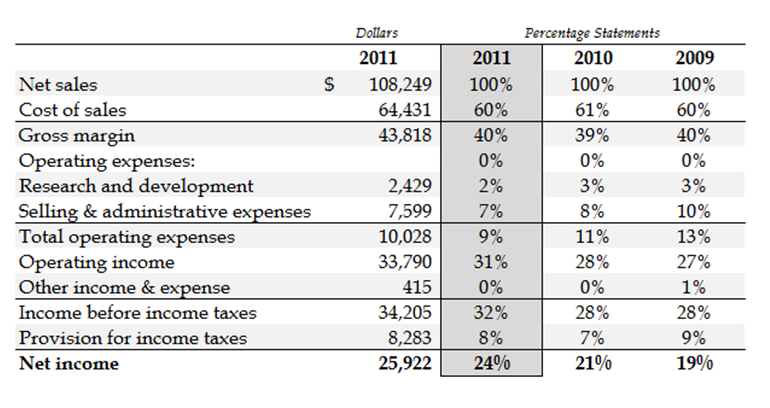
Formula for Calculating Net Income Component Percentage
Net profit margin is one of the most important indicators of a company’s financial health. By tracking increases and decreases in its net profit margin, a company can assess whether current practices are working and forecast profits based on revenues. It’s generally desirable that the business enjoy growing, or at least steady, profit margin. Instead, if Acme’s margin sat at 22% in the prior fiscal year before falling to 15% last year, then it’s worth a shareholder looking into why income fell so dramatically as a percentage of revenue.
What Is Net Income Component Percentage Used For?
Net profit margin also subtracts other expenses, including overhead, debt repayment, and taxes. A component percentage analysis shows the relationship between specific line items on a financial statement and the total amount on the statement. For example, to calculate the net income, take the total sales and subtract expenses and taxes. To show the relationship between the line item – sales and the total amount that includes the line item – and net income, you divide net income by total sales.
- If you look at an income statement template, you can find it at the bottom as the value in the bottom line.
- You may be tempted to think that the higher your net profit margin, the better for you.
- The net income of a company can be a misleadingly measure of profitability and portrayal of its current financial state from a liquidity and solvency standpoint.
- ” However, offering discounts results in major benefits, like increased sales and customer loyalty.
- This is why investors use net margin for running financial analysis and making investment decisions.
What Is Net Profit Margin?
The net profit margin illustrates how much of each dollar in revenue collected by a company translates into profit. The Percentage of Net Sales Method works by assigning a cost to each item in the ending inventory equal to the percentage of net sales realized from that item during the period. When an item is sold, it is given a cost equal to its assigned percentage multiplied by the total net sales for that period. This method is often referred to as the income statement approach because the accountant attempts, as accurately as possible, to measure the expense account Uncollectible Accounts.
A high percentage means that the company did well in managing its expenses. It is also useful to compare it to a benchmark, such as industry average or past performance, to determine the company’s standing. Founded in 1993, The Motley Fool is a financial services company dedicated to making the world smarter, happier, and richer. The Motley Fool reaches millions of people every month through our premium investing solutions, free guidance and market analysis on Fool.com, top-rated podcasts, and non-profit The Motley Fool Foundation.
Importance of net profit margin
If your operating costs grow at a rate faster than revenue, the net profit margin will decrease. This is why investors use net margin for running financial analysis and making investment decisions. Companies with increasing net margins attract investors and see share price growth over time. From the gross profit line item, the premium tax credit the next step is to subtract operating expenses, resulting in the company’s operating income, or earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT). Net income margin is the net after-tax income of a business, expressed as a percentage of sales. It is used in ratio analysis to determine the proportional profitability of a business.
On the other hand, gross income can be equated with total sales before any deduction of expenses. Further, operating income is the amount of money left over from revenues after operating costs and the cost of goods sold have been deducted, but before income taxes and interest expenses are taken out. Net profit ratio (NP ratio) is a popular profitability ratio that shows the relationship between net profit after tax and net sales revenue of a business entity. It shows the amount of profit earned by an entity for each dollar of sales and is computed by dividing the net profit after tax by the net sales for the period concerned. Both the numbers needed to calculate this ratio can be taken from entity’s income statement or profit and loss account. Net profit margin measures the amount of net income or profit you generate from sales revenue.
A negative net profit margin indicates that a company’s expenses and costs exceed its revenue, resulting in a net loss. This situation may raise concerns about the company’s financial viability and profitability. Also, the net income margin of different enterprises varies significantly across industries. For example, information services in the U.S. reveal, on average, a fairly high net profit margin ratio of about 13.4%. At the same time, the shipbuilding industry is characterized by a negative value of this indicator, -1.8%. Net profit ratio should be applied in your analysis with caution, because a low ratio may not always be a sign of bad operational performance.





